Paleolithic dieting is all the rage these days. I’m no expert on the paleo-diet, but–as I understand it–this refers to the practice of eating the foods consumed by our pre-agrarian ancestors. The idea is that if one consumes the foods that our species is evolutionarily-optimized to eating, one will be healthier. Whether one believes in the merits of the paleo-diet or not on the whole, it’s hard to argue that one wouldn’t be better off eating less highly-processed and highly-refined foods and more things that look like food at a glance.
Our diet isn’t all that has changed since the days of our pre-agrarian ancestors. Modernity has brought with it an entirely new way of experiencing stress. Eliminating or reducing stress is a common topic of discussion, but not all stress is created equal. There’s a necessary form of stress, a stress that makes one better, stronger, faster, and smarter. We don’t want to willy-nilly eliminate stress; we want to reduce the wrong type of stress.
Our ancestors—like animals–experienced brief periods of intense stress (e.g. saber-tooth tiger attacks), followed by longer periods in which they were free of deadlines, carpools, and after-school activities. Now, no one likes to have a saber-tooth tiger stalking them. It’s unpleasant. Modern humanity has gone to great lengths to eliminate those short bursts of terror, but not without cost. (If you don’t believe me read Robert Sapolsky’s Why Zebras Don’t Get Ulcers.)
Whether or not you believe that eliminating acute instances of terrifying stress is bad for mankind, it’s hard to argue that modernity’s leveling process didn’t eliminate stress, but instead resulted in a chronic stress on a smaller scale. People today have impossibly long daily to-do lists, and they have to accept trade-offs between work, family, and personal development.
It’s true that you don’t get eaten by a giant cat when you drop the ball, but life is so packed diverse events that one may feel like one is dropping some ball constantly. If your boss thinks you’re a model employee, then your kids are probably going to need therapy. If you have a contented home life, your boss may have his or her eyes open for someone who can give the firm consistently 70+ hour work weeks. If you feel you’re doing alright on both the work and family front, your body and / or mind is probably a train wreck.
Chronic [mini] stress may feel better than acute [catastrophic] stress, but it takes its tolls in various ways. First, with our sympathetic nervous system (fight-or-flight reaction) constantly engaged our body’s power to heal itself is reduced. When the parasympathetic nervous system is engaged, the body devotes resources to long-term goals like getting healthier, but in stress mode activities not relevant to immediate survival shut down. This is a great system if you have periodic life and death stress, but is not so good if you’re under constant stress.
Second, chronic stress reduces sleep, and sleep is essential to one’s mental and physical well-being. There are a wide variety of symptoms associated with sleep deprivation such as forgetfulness, decreased concentration, decreased alertness, reduced reasoning ability, diminished problem-solving capacity, and depression—all of which can diminish our physical health through accidents, ailments, suicide attempts, and lack of energy for exercise.
Third, chronic stress can make one fat, with all the health issues that result. Some people use food as a coping mechanism. Other people eat too fast or choose their food poorly because of time constraints or because they are not mindful of eating as their monkey minds churn at a mile a minute. Then there is the more convoluted and complex issue of cortisol–a hormone released under stress that is linked to weight gain in at least some cases. Even if you don’t have a problem on the calorie intake side, the stressed individual may not do so well on the calorie burning side—either because of a lack of time to exercise or a lack of energy.
Modern humans are uniquely suited to chronic stress because we are the only species that achieves the same physiological stress response by remembering and obsessing about a stressful event as experiencing it. Abandoning the modern approach to living isn’t an option most are willing to entertain; but there are ways to combat chronic stress.
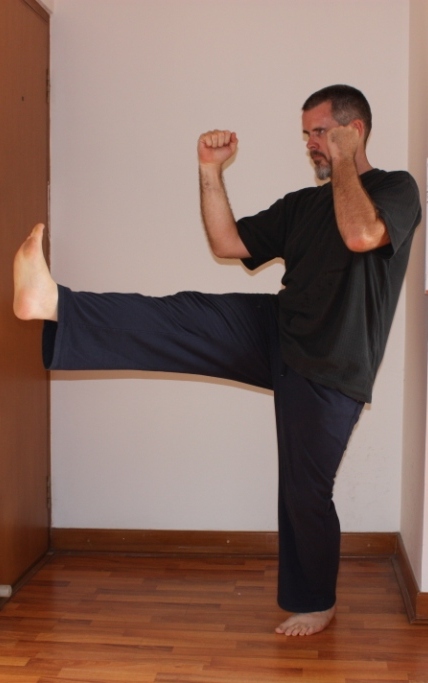
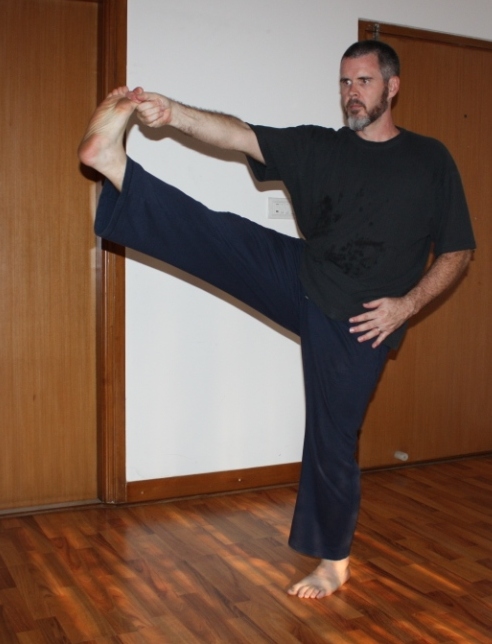
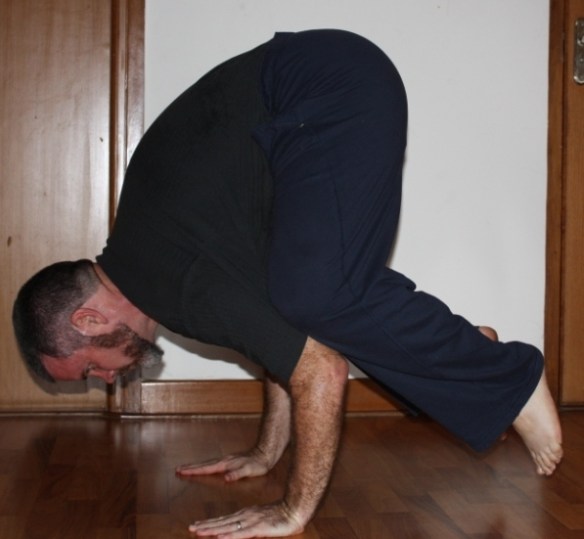
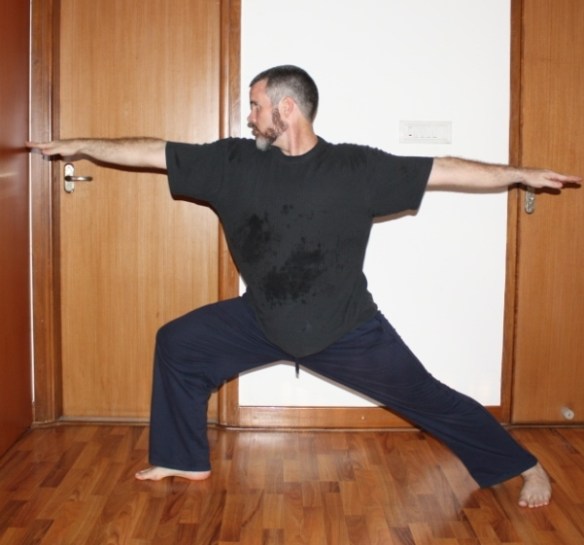
Move – Meditate – Mindfully Breath: The bad news is you’ve got to shoehorn these activities into your schedule daily (or at least several times a week.) The good news is that they don’t need to take up a lot of your day. There are a number of systems that address all three components in one handy package such as Qi Gong, Yoga, and some martial arts. I don’t think it matters so much which one chooses as how one goes about one’s practice.
Movement strengthens and strategically stresses the body, but it also increases one’s bodily awareness so that one becomes aware of how stress is manifesting itself in one’s body. Meditation teaches one how to live in the present moment, and it trains one to recognize the seeds of negative thought and emotion earlier so that one can counter-act them. Obviously, breathing is essential to life, but learning to be aware of one’s breathing patterns and to “manually override” the breath patterns associated with harmful emotional states is a beneficial skill.
Massage / Bodywork: Whether self-administered or other-administered (the latter allowing greater distressing–particularly if the masseuse is skilled) massage is an activity, like movement, that can help one become aware of where one is physically holding one’s stress. These physical manifestations of stress can exacerbate the whole experience of stress. One should take time periodically to have bodywork done. A day rarely goes by in which I don’t work on my own neck, shoulders, head, or face, and I occasionally get professional Thai Yoga Bodywork done.
The Places that Scare You: Force yourself to go someplace (not necessarily literally a “place”) that scares you once in a while. This needn’t be skydiving or hand-gliding—but it could be. It may be a martial arts class in which one has to put on the gloves occasionally and go at it. It may be joining Tostmasters and having to give a speech in front of a crowd. It may be traveling to some backwater where you don’t know the language, but you want to learn. This is a very personal issue. (i.e. A Type-A personality he-man may not find that skydiving is outside his comfort zone. If so, sorry, skydiving doesn’t count, he may need to learn ballroom dancing, or something else that truly takes him outside being comfortable.) KEY POINT: The problem with hiding from all stressors is that it doesn’t result in a stress-free life, what happens is that smaller and smaller stressors loom bigger and bigger in one’s mind. Which brings us to…
Perspective: One must put life’s challenges in perspective. Each person’s problems are important to them, and I don’t want to diminish anyone’s problems, but—come on—you’re not going to be eaten by a freaking saber-tooth tiger.