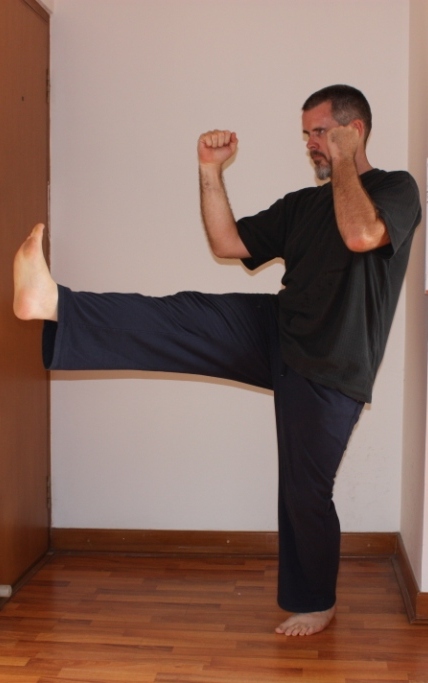
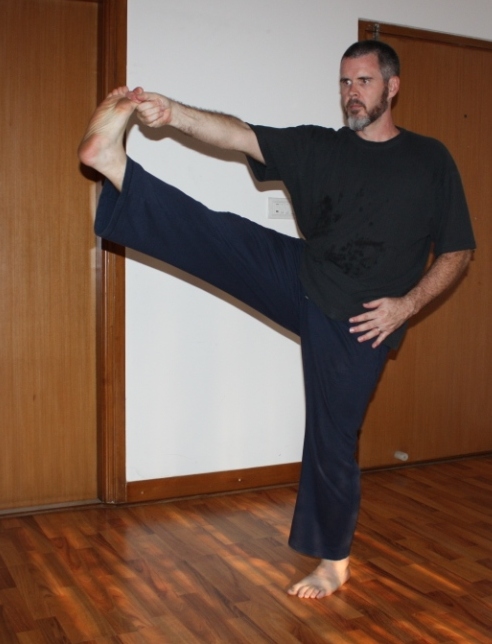
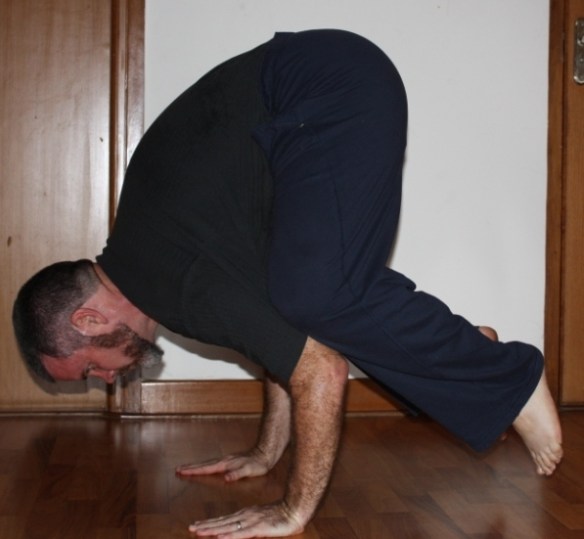
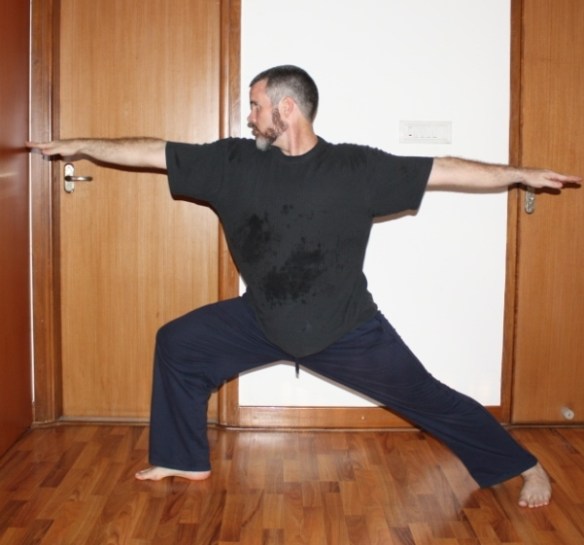
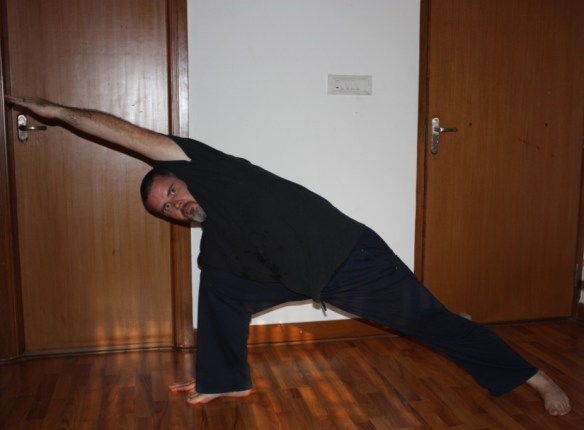
I see people staring at the railing on which they will stretch their hamstrings just like they would look at a side-by-side refrigerator unit that they have to move down a flight of stairs, psyching themselves up for the stretch. Or maybe they are weighing the question of whether they really need to stretch as one might ponder whether it would be better to get an engine overhaul or replace a car altogether. The point is that there seems to be an element of anxiety or dread associated with actions like stretching that aren’t necessarily pleasurable.
I have a theory about why this is the case.
First, people falsely equate discomfort with pain.
Second, the entire point of true pain is to tell one how not to move so as to avoid exacerbating an injury.
Third, this results in a desire to avoid pursuits that cause such physical discomfort.
Fourth, people create a self-fulfilling prophecy in which they tense muscles in the area of the stretch to counteract the aching stretch, but this just increases the discomfort level.
Your body has a clever little device called the myotatic reflex arc (MRA.) That’s when a muscle tenses to avoid injury because the muscle seems to be stretching too fast for comfort. However, that reflex is only relevant to dynamic movement and the fact that it’s a reflex arc means that the signals don’t go through the brain–thus–aren’t consciously controlled. The MRA is different from the tension one holds in a slow and controlled stretch. It’s fun to see people who’ve been encouraged to breath and relax into the stretch realizing that the stretch isn’t as bad as it seems.
Of course, many intense physical activities that cause discomfort may also result in a sufficient endorphin (natural painkillers) inflow and adrenaline / cortisol (stress hormones) outflow to result in net feelings of pleasure. While stretching results in endorphin release, the action of holding the muscle stretched may be too much for our natural painkillers to counteract, particularly when one is breathing easily and thus the body is not under the level of whole-body stress that might encourage the big endorphin dumps desired.
The problem is that one can’t achieve flexibility without pressing against one’s limits any more than one can make strength gains without lifting more or by employing more repetitions. If one just goes to the point at which one is no longer comfortable, you may be able to prevent losing flexibility, but you’re not going to make gains.
Another part of the problem is that people often go into stretching cold, and thus maximize their discomfort. Doing warm-ups and joint articulations before any kind of intense stretching is a good practice. These warm-ups should not test the fullest range of motion, but should move with sufficient quickness to get the muscles and the synovial fluid in the joints warmed up.
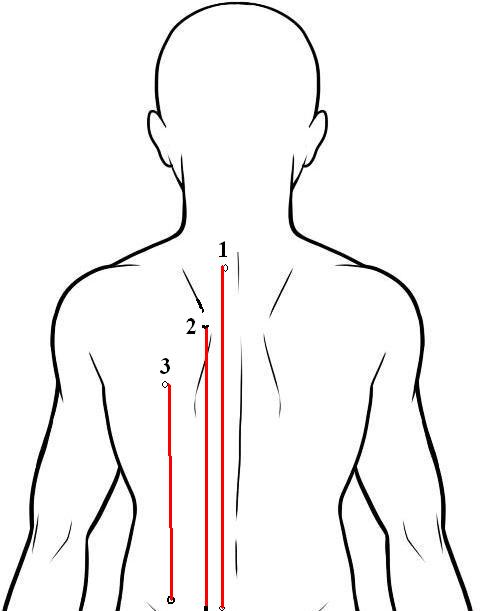
The problem with seeing stretching as painful is that it discourages it. Some individuals fail to stretch altogether, and others focus only on the major muscle groups (hamstrings and quads) and miss muscles that adduct, abduct, rotate, and generally stabilize and support the primary agonist or antagonist muscle pairing. The most common injury in the Japanese martial art that I study is a knee injury attributable in part to insufficiently flexible external rotators and abductors and the inability to keep the knee in line with the toes–thus putting too much torque on the joint and too much load on the ligaments.

Wrong: knee is not pointing over toes
Martial artists, in particular, need to avoid equating discomfort with pain. When discomfort becomes pain, pain becomes agony, and agony become intolerable. There are many factors that can determine the outcome of a combative event, including technical proficiency, physical fitness, and the ability to persevere. The last one may mean the ability to take a licking and keep on ticking as the Timex people used to say.
The good news is that it’s possible to rewire one’s brain to avoid equating the discomfort of stretching with pain.
Step 1: Get a yoga face. In the martial arts, we talk about having a warrior face, which is an expression that conveys one’s intensity and seriousness. For yoga and stretching one should ditch the agony face and replace it with a serene face. My personal recommendation is that you aim to emulate the faces on the Bayon at Angkor.

Yoga face as seen on the Bayon at Angkor
Step 2: Keep your mind on your breath, and away from the sensation of the stretch. There’s a reason yoga teachers harp on breath, it will help one reduce one’s overall tension.
Step 3: Stop using the word pain (in your own mind or when speaking out loud) to refer to the feeling of a stretched muscle. You may not be able to replace the word “pain” with something as euphemistic as “stretch bliss,” but try to avoid giving it a name with a negative connotation. It’s simply the sensation of a stretched muscle
Step 4: When you find yourself wearing an agony face and squeezing out the protective muscular tension, ease off the stretch until it’s comfortable. Then ease back into the stretch, keeping the surrounding muscles relaxed and the breath even and deep. You can visualize expelling the tension with one’s exhalation if that helps.
Step 5: When you experience real pain, have no guilt about heeding it and giving that part of the body time to heal. Of course, this requires an ability to differentiate stretch sensation from true pain.
Now I’ll segue into a discussion of actual pain. When I was having a lot of problems with my lower back–eventually diagnosed as arthritis–I had a bizarro interaction with my healthcare provider. When I first went to the doctor, I faced this unsubtle wall of suspicion because back injuries are a common fraud device for persons addicted to painkillers. That’s because there are many forms of back injury that are hard to witness externally. However, when they x-rayed my back they could see clear indication that something was wrong. Then they were surprised when they tried to foist painkillers on me, and I wasn’t interested.
Here is how I look at painkillers. Imagine the “check-engine” light came on in your car, and you took the vehicle to the mechanic. The mechanic has your car for a brief time and comes back to you with a nominal bill. At first you are thrilled, and then you ask the inevitable question, “So what was the problem?” Your mechanic then says, “Oh, I have no idea, I just disconnected the light. That light won’t be giving you any more trouble.” Needless to say, you are decidedly less thrilled. You wanted the underlying problem fixed.
Don’t get me wrong, I’m not saying that there’s no place for pain-killing medication. If one has pain that is so severe that one cannot rest, one’s body won’t be able to heal itself properly.
However, if you pop painkillers to do away with bodily aches, you should reconsider. Those aches are what being alive feels like, and if they come from exercise or labor they should be welcomed and not be framed in a negative light. If they are an indication of a postural misalignment or some sort of systemic problem, you should look into fixing the underlying problem.
[To be fair to my aforementioned doctor, I think people aren’t conditioned to the notion that they are the key participant in their own healthcare and that fixing problems will often require hard work on their part. So a part of the problem in some places–most notably America–is that healthcare isn’t profitable unless they are pushing surgery or expensive medications. However, another part of the problem is that people just want to go to the doctor and have the expert fix them without requiring the personal effort of fixing postural deficiencies or cutting weight. I can understand why doctors are a bit fed up with suggesting people do the work only to get no response. I saw a statistic recently that only 1 in 8 people threatened with a lethal illness would make a behavioral change recommended by a doctor to reduce the threat of the ailment–e.g. stop smoking, stop drinking, cut weight, etc.]
Share on Facebook, Twitter, Email, etc.
 Faster, Higher, Stronger: How Sports Science Is Creating a New Generation of Superathletes—and What We Can Learn from Them by Mark McClusky
Faster, Higher, Stronger: How Sports Science Is Creating a New Generation of Superathletes—and What We Can Learn from Them by Mark McClusky