In September I attended the General Thai Massage and Foot Massage courses at Wat Po. The teacher from whom I first learned Thai Massage (a.k.a. Thai Yoga Bodywork or Nuad Bo Rarn) was trained in Chiang Mai by various teachers, and the style he teaches reflects that northern heritage. I was curious to see how the style of massage varied in the south from the northern approach that I had already learned. Would I be in uncharted waters? Or would the Wat Po course merely be a refresher of what I had already learned? These questions were on my mind as I began the course.
The answer turned out to be somewhere in between. The Wat Po approach wasn’t radically different from what I had already learned, but neither was it a carbon copy. One could clearly see the common origin of these styles. For yoga practitioners, a reasonable comparison would be to imagine you studied Bihar yoga, and then you sat in on an Ashtanga Vinyasa class. Most of the postures would be similar if not the exact same—e.g. a downward dog is a downward dog. However, the sequence is a little different, you may run into a posture or two that you hadn’t seen before, and there will be many little differences in points of emphasis and so on. The same could be said of two martial arts that have a recent common ancestor art. (However, I think martial arts evolve more rapidly than other systems of movement because there is a life and death urgency to adapt to local conditions, and so martial arts can diverge rapidly.)
I won’t get into every little difference in this post. For one thing, the first course I took was a 60 hour (10 day) course, and the Wat Po course was only half as long (5 day / 30 hours.) Therefore, some of the apparent differences might have more to do with the need to conform to time limitations than true stylistic differences. The Wat Po course was designed to impart a sequence that could be done in an hour-and-a-half bodywork session. The first course I took taught some material that was redundant in the belief that one could tailor one’s sequence to the recipient’s needs and / or the masseuse’s preferences.
As an example, at Wat Po we didn’t learn any massage of the chest or abdomen, but I was shown (in fact, I was recipient of) the Wat Po approach to abdominal massage and it was pretty much the same as I’d learned previously. In my earlier learning, the approach to energy lines was to stretch (longitudinally) the limb, then apply palm pressure, then work the line (typically with the thumbs), and then one would repeat the palm pressure and finish with a repeat of the stretch. At Wat Po, they went straight for the energy line (sen) and followed that with the palm pressure work. I have no way of knowing whether this difference was more due to timing or style.
Before getting into the differences, I will talk a little about similarities. The general approach was the same (e.g. the recipient is fully clothed in a light, comfortable garment(s)) and the massage is ideally given on a thin, dense mattress/pad on the floor–rather than on a table. The general principles of sequencing were the same. Namely, one began at the feet and worked in the direction of the head. Also, when working on a limb, one began at the distal end, worked toward the torso, and then back toward to the starting point. Also, energy line work was done before the stretches. There were four positions in both styles: supine, side, seated, and prone, and—unlike many other forms of massage—the supine position was at the fore (i.e. neither style emphasized the prone position and back work over the supine in the way other varieties of massage often do.) Both styles of massage (as probably all massage) began with a brief introduction and questioning designed to make sure the individual didn’t have any contraindicated conditions. Both styles of Thai massage began with a moment of prayer or contemplation—this is similar to some styles and different from others and speaks to the traditional nature of Thai massage.
The side and seated sequences were the most similar between the two styles. I learned more in these sequences in the longer (Chiang Mai) course, but what was included in the Wat Po course was largely the same. Where the stretches were of the same type, they tended to be virtually identical. By that I mean to say that both styles had stretches that weren’t taught in the other style, but where that was not the case, the stretches were indistinguishable. For example, the pictured variant on sarpasana / bhujangasana [snake / cobra backbends] was done in the same manner in either style. (I learned more stretches in the first—Chiang Mai–course, because it was longer.) Over all, the energy lines (sen) tended to be identical, but there weren’t always the same number of them, nor were the same ones always emphasized. There were some differences in the feet lines that I’ll get into below.
Now let’s get to the differences. Starting with some small differences, the manner of palm pressure work was different between the two systems. In the Wat Po style, there was always one fixed point that one hand locked in place while the other hand applied palm pressure. I had previously learned to use both hands in a rhythmically alternating series of palm pressure applications.
One little difference that I found interesting involved the technique of closing the little flap over the ears at the end of the face and head massage (both styles close off the ears.) I had been taught to very gently release pressure so as to avoid any kind of popping that might disturb the recipient. However, at Wat Po the instructor taught to vigorously pull the fingers away—resulting in a pop. My guess would be that the idea was to get the recipient’s attention so that one could transition them from the face massage (which notoriously puts people to sleep) to a wakeful state so they could follow instructions for the stretches that followed. (We were taught face massage as part of the seated sequence. Previously, I had learned that this was an option, but that it was easier to do the face massage from supine so you didn’t have to worry about the recipient falling asleep and possibly falling over literally.
A final little difference was how the blood stop was done for the lower extremities. At Wat Po, they did the leg blood stop with both legs straight, whereas I had previously learned this technique with an open groin, i.e. the knee pointed out. (Both ways work about the same, but I think it might be a little less awkward to do it with the groin open as one is not in as close of proximity to the recipient’s privates.) The blood stop for the arm was identical.
The energy lines are one of the most fundamental aspects of Thai massage, and one would expect little variation in them between styles. This proved largely, but not entirely, true. For example, the leg lines were the same (as one might expect because one cannot stray too far from some lines without getting onto bone.) Also the points at the top of the shoulder, around the neck, the base of the skull, and the scapulae were the generally the same–except more or fewer points might be employed from one style to the other.
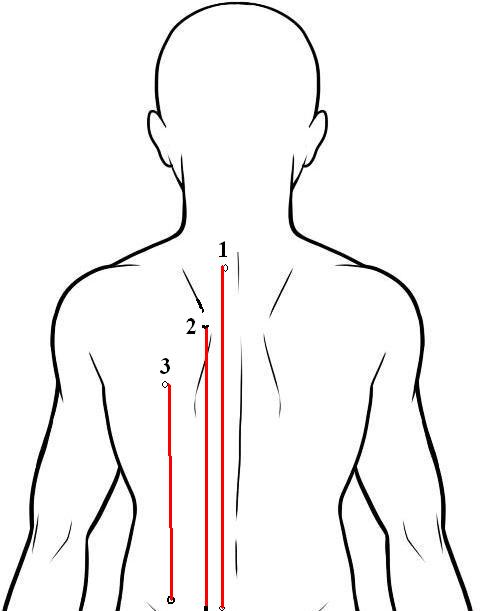
The arm lines were almost the same. The line on the back of the arm was the same, and the line that goes up the middle of the inner arm was the same. However, there was a second inner line that ran in line with the little finger along the lower edge of the arm (presuming the arm is straight out from the shoulder as it is for massaging the inner arm in both styles.) The lines of the back that were used were different. In my (not very accurate) diagram, the lines 1 and 3 were emphasized in the Chiang Mai style, but 1 and 2 were the lines used in the Wat Po system.
The greatest divergence in lines and points was in the area of the feet. The best example of this can be seen in the lines of the sole. In the Chiang Mai style I’d previously learned there were five lines that radiated from a point where the heel transitioned into the arch about midway across the foot and went toward the base of each toe. The Wat Po style had three lines that were more or less parallel in line with the big toe, middle toe, and the little toe. See diagrams.
In summary, the difference between these two styles wasn’t that great. In many cases the techniques were exactly the same, in most they were marginally different, and only rarely were they completely different. I don’t really have a preference between the two styles. I think which would be a better experience comes entirely down to the skill of the masseuse / masseur.